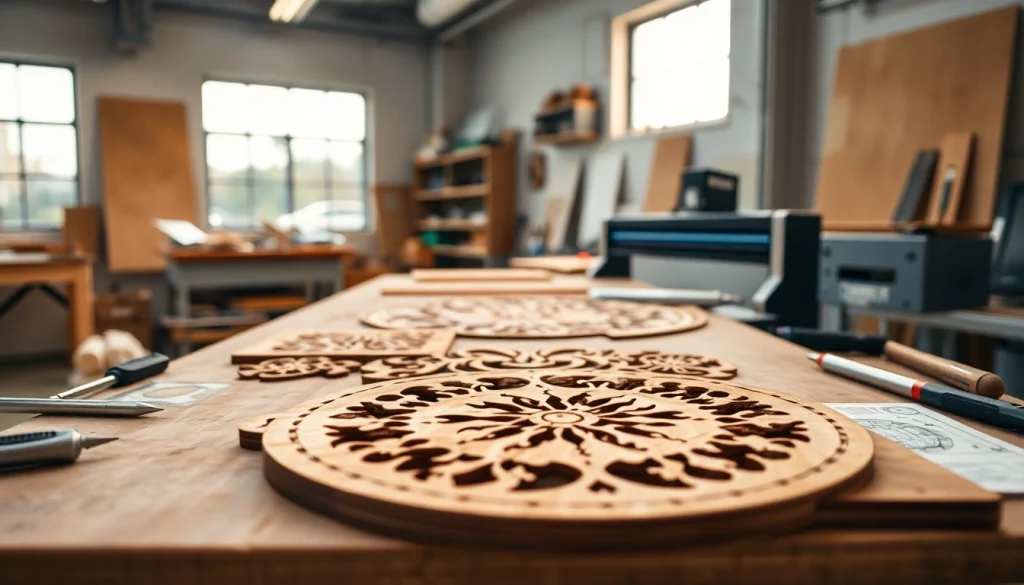
Introduction to Laser Cutting Designs
Laser cutting has revolutionized the way we approach design and manufacturing. With precision and versatility, it allows creators to transform a plethora of materials into intricate designs that cater to various applications. Whether in fashion, architecture, or crafting, the possibilities are endless. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of laser cutting designs, including their history, process, and impact across diverse industries.
What Are Laser Cutting Designs?
Laser cutting designs refer to the stunning patterns and shapes created using a laser beam that cuts through various materials with high accuracy and speed. This process utilizes a focused laser to engrave, cut, or mark materials, making it an essential technique for manufacturers, artists, and hobbyists alike. The designs can range from simple shapes to complex art pieces, tailored for specific uses or decorative purposes.
History and Evolution of Laser Cutting
The concept of laser cutting dates back to the 1960s when lasers were first developed. Initially used for military and medicine, the technology quickly found its way into industrial applications by the late 1970s. Over the decades, advances in laser technology have led to enhanced effectiveness and reduced costs, making it accessible to smaller firms and individual creators. Today, laser cutting is not just a method of production but an integral aspect of design innovation across multiple sectors.
Applications in Various Industries
Laser cutting has a broad range of applications which include:
- Manufacturing: Used for producing components, creating prototypes, and fabricating products with high precision.
- Fashion Design: Applied to cut intricate patterns in fabric or leather, providing unique textures and designs that elevate fashion items.
- Architecture: Employed to produce detailed models, architectural features, and decorative elements that enhance building aesthetics.
- Arts and Crafts: Artists utilize laser cutting for creating detailed artwork, signage, and personalized gifts.
- Jewelry Making: Allows for the creation of intricate designs in various materials such as metal and acrylic.
Understanding the Process of Laser Cutting
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting operates by directing a high-powered laser beam onto a material, which either melts, burns, or vaporizes the material along the desired path. The process begins with generating a laser beam, which is then focused through lenses to achieve a precise thickness. The material is placed on a flat bed, and the cutting head, controlled by a computer-aided design (CAD) program, moves across it to deliver a finely focused laser beam to cut shapes with exactitude.
Types of Laser Cutters
There are several types of laser cutters commonly used in the industry:
- CO2 Lasers: Highly versatile and effective for cutting non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and fabric.
- Fiber Lasers: Utilize solid-state technology to cut metals with high efficiency, producing high-quality cuts.
- YAG Lasers: Typically employed for detailed engraving and cutting in harder materials.
- Crystal Lasers: Known for their precision, often used for high-accuracy applications.
Materials Used in Laser Cutting Designs
Laser cutting can be performed on a variety of materials, each contributing unique characteristics to the final design:
- Wood: Ideal for custom furniture, decor, and intricate designs.
- Acrylic: Perfect for signage, display cases, and artistic projects with vibrant colors.
- Metal: Suitable for industrial applications and elegant jewelry pieces.
- Leather: Used in fashion, upholstery, and accessories.
- Paper and Cardboard: Excellent for creating prototypes, packaging, and crafts.
Design Principles for Laser Cutting
Creating Effective Laser Cutting Designs
To create stunning laser cutting designs, consider the following principles:
- Contrast: Ensure a strong visual contrast between cut and uncut areas to highlight the design effectively.
- Scale: Maintain proportion in design elements to ensure functionality and aesthetic appeal.
- Details: Incorporate fine details that the laser can achieve without compromising structural integrity.
- Material Selection: Choose suitable materials that complement your design and fit your intended purpose.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While designing for laser cutting, avoid these common pitfalls:
- Overly Complex Designs: Intricate details may lead to weak spots; simplicity and clarity are key.
- Neglecting Material Properties: Not accounting for different materials can result in undesirable outcomes.
- Ignoring Kerf: Failing to consider material thickness can lead to inaccuracies in the final product.
- Poor File Preparation: Insufficiently preparing files for cutting can lead to errors during the process.
Best Design Software for Laser Cutting
Utilizing the right software can significantly enhance your laser cutting experience. Some of the best design software includes:
- Adobe Illustrator: Ideal for vector design and supports various file types for laser cutting.
- Inkscape: A free alternative, perfect for creating detailed vector illustrations.
- CorelDRAW: Popular among professionals for its extensive design capabilities.
- Autodesk Fusion 360: Great for 3D modeling and complex designs, especially in manufacturing.
Enhancing Laser Cutting Designs
Techniques to Boost Visual Appeal
To make your laser cutting designs more eye-catching, consider these techniques:
- Layering: Overlapping different materials or designs can create a three-dimensional effect.
- Engraving: Adding engraved textures or patterns gives depth to the design.
- Color Mixing: Utilize colored materials or finishes to enhance visual interest.
Combining Laser Cutting with Other Techniques
Combining laser cutting with other methods can yield remarkable results. Techniques include:
- Etching: Use lasers to etch designs on surfaces for a more refined appearance.
- Assembly: Join laser-cut parts with traditional crafting methods for innovative mixed media projects.
- Incorporating Technology: Integrate LED lighting into designs for dynamic visual effects.
Case Studies of Unique Projects
Real-world examples can illustrate the potential of laser cutting designs:
- Art Installations: Artists have created breathtaking installations featuring laser-cut sculptures that play with light and shadow.
- Architectural Features: Buildings have utilized laser cutting to produce intricate facades that enhance functionality while being visually striking.
- Fashion Lines: Designers have launched collections featuring laser-cut fabrics that revolutionize the fashion landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions about Laser Cutting Designs
What materials can be used for laser cutting designs?
Materials such as wood, acrylic, metal, leather, and fabric can be effectively cut using laser technology.
How do I ensure the best quality in my laser cutting designs?
Optimize designs by considering material properties, file preparation, and machine settings to ensure high-quality outputs.
Can I create custom designs for laser cutting?
Yes, custom designs can be created using design software that supports vector files, ideal for laser cutting.
What safety precautions should I take?
Always wear protective eyewear, handle materials with care, and ensure proper ventilation while operating laser cutting machines.
How do I maintain my laser cutter for optimal performance?
Regularly clean and check optics, calibrate settings, and replace worn components to keep your laser cutter performing efficiently.